The Health Benefits of Fennel: A Crisp and Flavorful Nutritional Powerhouse
Introduction
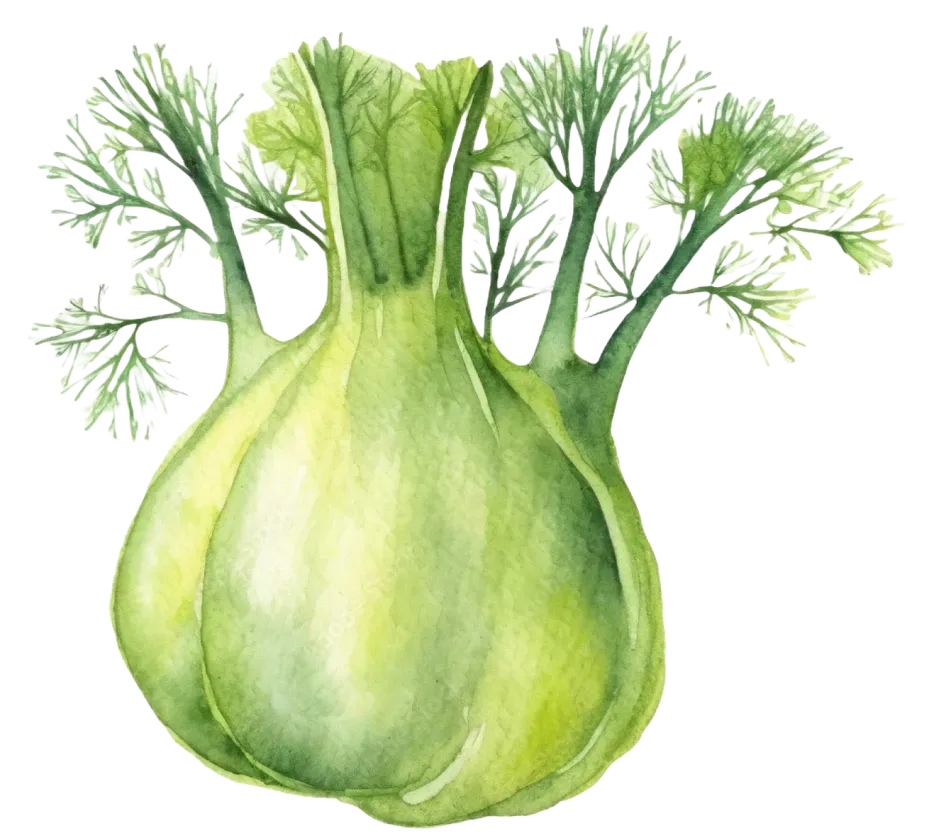
Fennel is a fragrant, crunchy vegetable known for its mildly sweet and licorice-like flavor. Both the bulb and seeds are used in culinary and medicinal applications worldwide. Whether roasted, sautéed, or eaten raw, fennel adds a burst of flavor and a host of nutrients to dishes. From its fiber content to its unique antioxidant profile, fennel offers numerous health benefits that make it a nutritious addition to your diet.
Health Benefits of Fennel
- Supports Digestion
Fennel is a rich source of dietary fiber, which promotes healthy digestion by aiding in regular bowel movements. Additionally, fennel seeds are often used as a digestive aid to help reduce bloating, gas, and discomfort after meals.
- Rich in Antioxidants
Fennel is loaded with antioxidants, including flavonoids, vitamin C, and quercetin, which help neutralize free radicals in the body. These antioxidants help reduce inflammation and protect cells from oxidative damage, supporting overall health and longevity.
- Boosts Immune Function
The high vitamin C content in fennel helps support a strong immune system by enhancing the body’s ability to fight infections. Regular consumption of vitamin C-rich foods like fennel can reduce the risk of common colds and flu.
- Supports Heart Health
Fennel contains potassium, which is essential for regulating blood pressure. In combination with its fiber content, fennel helps lower cholesterol levels and supports overall cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Promotes Bone Health
Fennel is a good source of manganese and calcium, both of which play key roles in maintaining strong bones. Including fennel in your diet can help prevent bone loss and support skeletal health, especially in aging individuals.
Creative Ways to Enjoy Fennel
Fennel is a versatile ingredient that can be enjoyed in both raw and cooked forms:
- In Salads: Add thinly sliced fennel to salads for a crisp, refreshing crunch that pairs well with citrus fruits, arugula, or walnuts.
- Roasted: Roast fennel bulbs with olive oil, salt, and herbs for a sweet and caramelized side dish.
- In Soups and Stews: Add chopped fennel to soups and stews for an aromatic base that enhances the flavor of the dish.
- Sautéed: Sauté fennel with garlic and lemon for a flavorful, nutrient-packed side.
- As a Tea: Brew fennel seeds in hot water to create a digestive aid tea that helps soothe stomach discomfort and improve digestion.
Conclusion
Fennel is a nutrient-dense vegetable that offers a range of health benefits, from supporting digestion and heart health to boosting immune function and promoting strong bones. Whether eaten raw in salads, roasted as a side dish, or brewed into a soothing tea, fennel is a versatile and flavorful addition to any meal. Incorporating fennel into your diet is an easy way to enhance both taste and wellness.
FAQs About Fennel
- Is fennel good for weight loss?
Yes, fennel is low in calories and high in fiber, making it a filling food that supports weight management.
- How should I store fennel?
Store fennel bulbs in the refrigerator, wrapped in plastic or stored in a plastic bag, for up to five days.
- Does fennel lose nutrients when cooked?
Fennel retains most of its nutrients when roasted or sautéed. However, boiling it for extended periods may reduce its vitamin C content.
- Is fennel AIP diet compliant?
Yes, fennel is compliant with the AIP diet and can be enjoyed by those following the autoimmune protocol.
- Is fennel Low-FODMAP?
Fennel can be Low-FODMAP in small portions, but larger amounts may contain moderate levels of FODMAPs.
- Is fennel Low Histamine?
Fennel is generally considered low in histamine and is well-tolerated by individuals with histamine intolerance.
- Is fennel Keto-friendly?
Yes, fennel is keto-friendly due to its low carbohydrate content, making it an excellent addition to low-carb and ketogenic diets.
Recipes: